1. As the operating temperature increases the design stress decreases
2. When radio graphic tests are conducted for pressure vessels, the joint efficiency is 0.85 for spot radiography and 1.00 for 100% radiography.
3. For stainless steel materials the corrosion allowance is zero.
4. For elliptical heads the ratio of major axis to minor axis is 2:1
5. What losses are taking place in the storage of volatile liquids? Evaporation losses, filling losses, breathing losses.
6. What is TEMA? Tubular Exchangers Manufacturers Association, USA. Heat Exchanger design and fabrication Code.
7. Corrosive fluids are passed through tube side of a shell and tube heat exchanger
8. Baffles are provided in agitated vessels to prevent swirling.
9. For triple effect evaporators the economy is approximately three.
10. Heat transfer coefficient has the units of W/ (m2.K) in SI.
11. Plate thickness: hole diameter is between ______:______ for sieve trays
12. At minimum reflux ratio infinite number of plates are required for distillation.
13. Define loading
14. A redistributor is used for every 3D (i.e., 3 times the diameter of height) of the packed section.
15. In a dryer, number of flights ranges from _____D to _____D where D is in feet.
16. Define cut size for a cyclone separator. (The minimum diameter of particle that can be collected with 100% efficiency)
17. Formation of new crystals is termed as __________.
18. What is an induced draft cooling tower? (Air is sucked by the fans at the top of the tower)
19. Indicate any two advantages of pressure filter
20. Define critical speed of centrifuge.
21. Floating head Heat exchanger is used for large temperature differentials
22. Why triangular pitch is preferred than square pitch in tube layout in heat exchanger?
23. Differentiate between evaporation and drying
24. Fourier's law applies to _________
25. Fruit juice can be concentrated in _________ evaporator
26. The most common standard size of a bubble cap is marketed with _________ inches diameter cup and _________ inches riser
27. Azeotropic distillation is employed to separate _________ mixture
28. Leaching is applicable to _________ system
29. Flooding occurs in a column due to _________
30. Reboiler is considered as one theoretical plate because _________
31. Relative humidity is the ratio of vapor pressure of high volatile component, vapor pressure of low volatile component
32. Milk is dried to powder in _________ dryer
33. For continuous drying of granular materials we use _________ dryer
34. Crystal size in a continuous crystallizer depends upon _________, _________, and _________
35. In case of cooling towers the ratio of rates of heat and mass transfer is indicated by Lewis number
36. Reaction vessels with the same thickness of shell but smaller in diameter withstands higher pressure
37. Write an equation for power requirements for an agitator
38. Draw a diagram of a concrete vessel for storing solids
39. Under what conditions of liquids, vacuum drum filters are used?
40. What is meant by maximum yield stress of a metal?
41. A pump operating under specified conditions delivers insufficient quantity of fluid. How it can be set right?
42. Differentiate between the efficiency of venturi meter and orifice meter
43. Define overall heat transfer coefficient in heat transfer
44. Define HTU and NTU
45. What is meant by weeping in a distillation column? How it can be eliminated?
46. What is meant by unbound and bound moisture in a solid?
47. Draw a line sketch of a top-driven centrifuge
48. Why cooling towers are used in process industries?
49. Suggest a suitable type of storage vessel for storing liquid ammonia. Give reasons for such recommendation.
50. What is meant by steam economy in the design of evaporators?
51. What is meant by filter cake resistance? How it affects filtration?
52. Give an equation for the calculation of power requirement for an agitator
53. Mention various types of commercially available crystallizers
54. Mention why different packings are used in a distillation or absorption tower
55. Define adsorption phenomenon
56. Why steam traps are used in heat transfer apparatus?
57. What type of closures are used for pressure vessels? Why?
58. What are the differences between condenser and a reboiler?
Common Things:
In both the cases phase change takes place and both operations require some media i.e. in condenser for cooling and in reboiler for heating.
Differences:
In condensers latent heat removed from the vapor using a coolant and phase change takes place from vapor to liquid
In reboilers latent heat provided for the liquid using a heating media and phase change takes place from liquid to vapor
59. Why low pressure steam is used in evaporators?
For steam (Go through steam tables) as pressure increases Latent heat decreases and specific heat decreases. Latent heat can be recovered and where as specific heat cannot be utilized fully.
So for more steam economy low pressure steam is desirable.
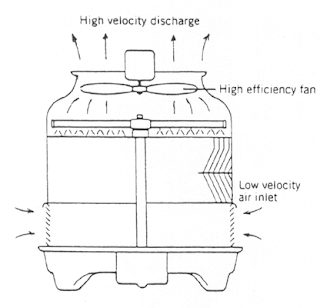
60. What is meant by induced draft in cooling tower?
Induced draft means we create (induce) some pressure draft (difference) using I.D Fans (Induced draft Fans) on the top Cooling tower.
Here we use a high efficiency fans to suck the air from the bottom of the cooling tower and it discharges air to atmosphere at high velocities. Typical Induced Draft cooling tower is as shown in the figure.
During this movement of air from bottom to the top of cooling tower water comes in contact with air in counter current direction and cooling of water takes place by means of evaporation cooling.
“By using any of the cooling towers we can cool the water up to its wet bulb temperature of the environment.”
61. What is meant by CPU?
62. What are the various output devices?
63. What is an assembly language?
64. What is meant by Hierarch in computer operations?
65. What is meant by dew point?
66. Differentiate between ideal and nonideal mixtures.
67. What is an azeotrope?
68. Define activity coefficient.
69. What are the disadvantages of a fixed tube sheet heat exchanger?
Fixed type heat exchanger is one type of shell and tube heat exchanger tube sheet i.e. tube sheet is permanently welded or attached to the shell.
Disadvantages:
It is not possible to clean on the shell side of this exchanger.
It is not possible clean the tube bundle outside portion.
70. What ranges of velocities are to be considered for gases in heat exchangers?
71. Define boiling point elevation?
When we add solute to the solvent boiling point of solution will be more than that of pure solvent.
The difference between the boiling points of solution to that of solvent is known as boiling point elevation.
Example;
Aqueous sugar solution boiling point is more than that of pure water.
Phenomena:
We know that vapor pressure is directly proportional to the surface of the free liquid surface. When we add solute to the solvent free liquid surface decreases and in turn vapor pressure also decreases. So boiling point increases with the addition of solute to the solvent.
72. Differentiate between an evaporator and a reboiler.
73. What are the standard lengths adopted in shell and tube heat exchangers?
74. What is the function of the downtake pipe in a calendria evaporator?
75. What are the advantages of backward feed in multiple effect evaporation?
76. What is absorption factor?
77. Name the methods used for the determination of number of plates for multi component systems.
78. Name the types of trays used for distillation operation?
The terms "trays" and "plates" are used interchangeably. There are many types of tray designs, but the most common ones are:
Sieve Trays
Sieve trays are simply metal plates with holes in them. Vapour passes straight upward through the liquid on the plate. The arrangement, number and size of the holes are design parameters.
Because of their efficiency, wide operating range, ease of maintenance and cost factors, sieve and valve trays have replaced the once highly thought of bubble cap trays in many applications.
Bubble cap Trays
A bubble cap tray has riser or chimney fitted over each hole, and a cap that covers the riser. The cap is mounted so that there is a space between riser and cap to allow the passage of vapour. Vapour rises through the chimney and is directed downward by the cap, finally discharging through slots in the cap, and finally bubbling through the liquid on the tray.
Valve trays
In valve trays, perforations are covered by liftable caps. Vapour flows lifts the caps, thus self creating a flow area for the passage of vapour. The lifting cap directs the vapour to flow horizontally into the liquid, thus providing better mixing than is possible in sieve trays.
79. What assumptions are implied in the McCabe and Thiele method?
80. What methods are available for the determination of equilibrium data of nonideal mixtures?
81. Explain briefly the elements of a digital computer
82. What are the different operating systems used in computer?
83. What does Hierarchy mean in computer operations?
84. What are the various input devices?
85. Explain the term 'assembly language'
86. State the various thermodynamic properties of a binary mixture
87. When do you use steam distillation?
88. Explain briefly the use of vapor-liquid equilibrium data
89. Explain how do you estimate the density of a gas mixture
90. Define the term entropy and enthalpy
91. Graphically represent how temperature profile varies with distance in a counter-current heat exchanger
92. Define the term 'relative volatility' and indicate its importance in the design of distillation columns
93. Explain the term limiting liquid to gas ratio in a stripper
94. Define the term logarithmic mean temperature
95. State the advantage of using backward feed multiple effect evaporators over forward feed units
96. Explain briefly how minimum reflux ratio is determined in a distillation operation
97. State the assumptions made in McCabe-Thiele method of estimating the number of stages in a distillation column
98. Define the term 'number of transfer units' and 'height of transfer units' in a packed column absorber
99. Suggest what type of absorber do you use for absorbing hydrochloric acid gas
100. State the factors to be considered in the selection of a solvent for the given extraction operation
101. Define computer logic.
102. What are the different types of operational systems?
103. Explain time-sharing.
104. Name some commonly used high level languages.
105. What is a source program and object program?
106. Define activity and fugacity.
107. What is meant by a single pass and multi pass heat exchanger?
108. What are the different equations available for calculating VLE data?
109. What are the advantages of a double pipe heat exchanger?
110. Draw a neat sketch of a single effect evaporator.
111. When do you use finned tube heat exchanger?
112. On what basis are heat exchangers classified?
113. Evaporators are classified according to _________.
114. What are the accessories that have to be used with the evaporators?
115. Define elevation in boiling point.
116. What are the different types of tower packing?
117. What is Henry's law; where is it applied?
118. Define HETP.
119. Describe triangular diagrams.
120. Define correction factors; where is it used in heat exchanger.
Interview Questions on Mass Transfer Operations Click Here
Interview Questions on Fluid Mechanics Click Here
Interview Questions on Transport Phenomena Click Here


No comments:
Post a Comment